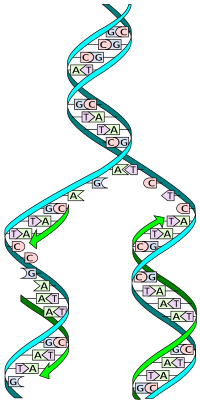
 During replication, the two strands are separated, and each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of a complementary counterpart strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication.
During replication, the two strands are separated, and each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of a complementary counterpart strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication.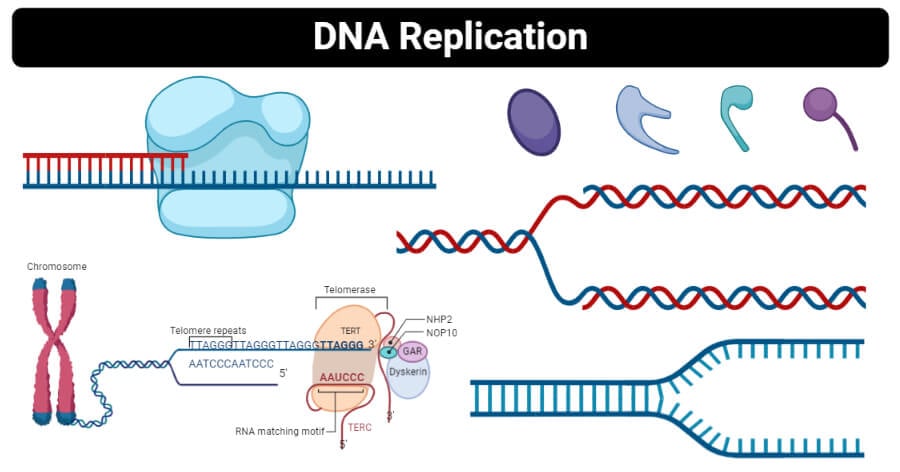 DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication is semi-conservative.
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication is semi-conservative.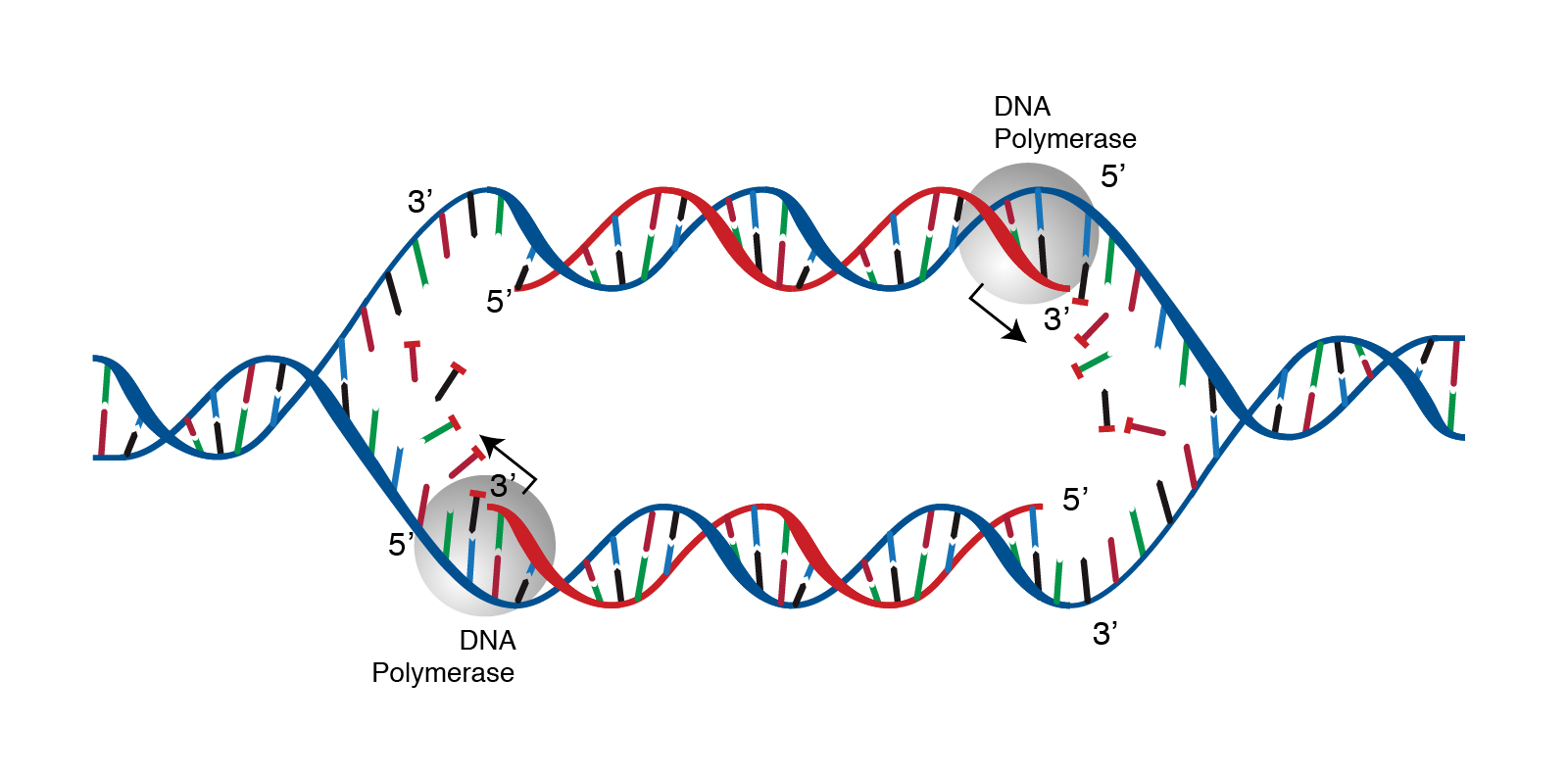 DNA replication is the process by which the genome’s DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome.
DNA replication is the process by which the genome’s DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome. In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the steps involved in DNA replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.
In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the steps involved in DNA replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.